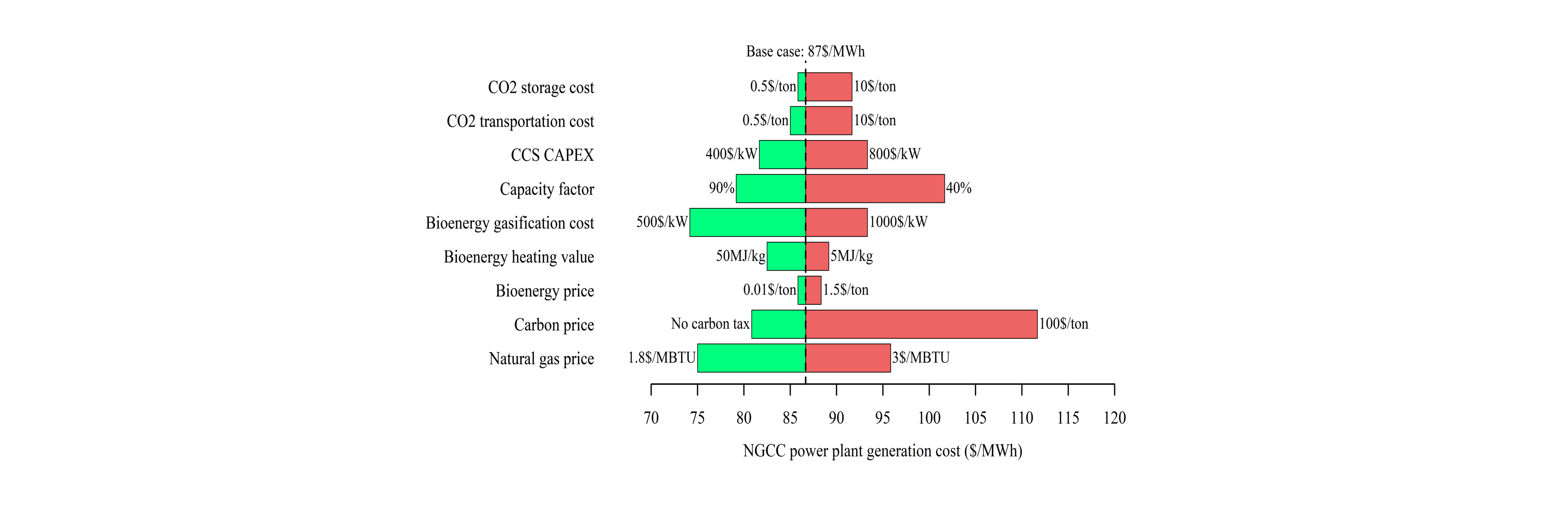
 Sensitivity of Natural Gas Combined Cycle (NGCC) Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) regarding various factors
Sensitivity of Natural Gas Combined Cycle (NGCC) Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) regarding various factors
The critical role of economic assumptions in cost-effectiveness analysis of power plant CO2 capture and storage
Abstract
Decarbonization of fossil fuel power plant has been identified as a key enabler on the 2DS climate change trajectory; Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is an important technology for such fossil fuel power plant decarbonization. Although the technology readiness level of CCS has become mature, successful demonstration projects are quite limited. Cost-effectiveness has been proved as a critical hinder of power plant CCS application. Recently, many studies conduct cost-effectiveness evaluation of fossil fuel power plant CCS; interestingly, the results differ a lot. A closer examination would find that these studies deploy divergent assumptions, such as fuel price, CO2 transportation cost; the following question is how these parameter uncertainties influence the power plant cost-effectiveness evaluation results and how could these analyses based on different assumptions be adapted to a consistent framework for comparison? In other words, global sensitivity of fossil fuel power plant CCS cost regarding to key economic parameters should be researched. Starting from here, we present a systematic analysis of the impact of key economic parameters on power plant CCS cost in this paper and point out how such impact should be addressed in future study.